How Is Dna Described and What Does This Mean
Nearly every cell in a persons body has the same DNA. DNA is a large complex molecule that allows cells to function and carries the genetic code that determines the traits of a living organism.
9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
It is a Nucleic Acid.
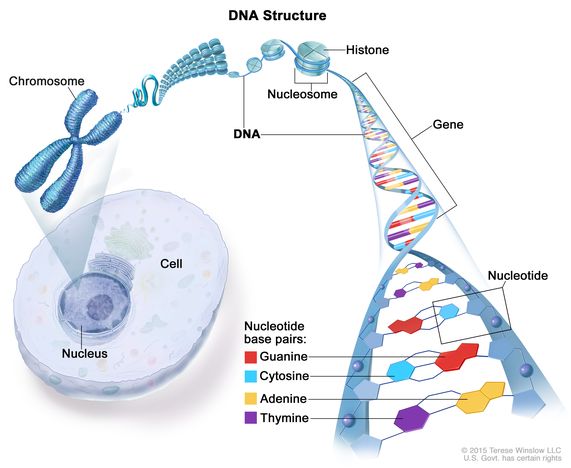
. DNA is in every cell of every living thing. DNA bases are read one at a time as they squeeze. A cellular structure containing genes.
DNA which stands for deoxyribonucleic acid is a molecule that supplies the genetic instructions that tell living creatures how to develop live and reproduce. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes in each body cell one of each pair from the. RNA is single stranded that contains ribose sugar and had uracil.
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the sequence of nucleotides within a DNA molecule. DNA Sequencing Definition. Overview of Steps in Analyzing DNA Evidence.
Most DNA is located in the. DNA is a structure that encodes biological information. The chromosome along with several proteins and RNA molecules.
DNA along with the instructions it contains is passed from. Several basic steps are performed during DNA testing regardless of the type of test being done. Typically DNA is found in the.
These nucleic acids are formed by the combination of nitrogenous bases sugar molecules and the phosphate groups that are linked by different bonds in a series of. The structure of DNA is dynamic along its. Deoxyribonucleic acid more commonly known as DNA is a complex molecule that contains all of the information necessary to build and maintain an organism.
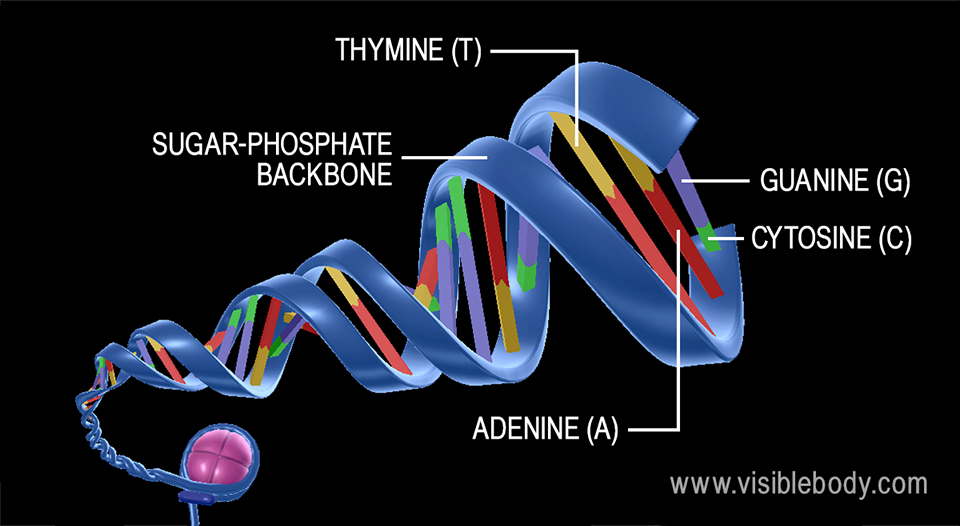
DNA is double helix and contains deoxyribose sugar and had Thymine. DNA deoxyribonucleic acid is a type of macromolecule known as a nucleic acid. It is shaped like a twisted double helix and is composed of long strands of alternating sugars and.
Nanopore-based DNA sequencing involves threading single DNA strands through extremely tiny pores in a membrane. Chromosomes are composed of DNA and proteins. Deoxyribonucleic DNA pronouced de-ok si-ribo-nu-kleik.
The DNA of most bacteria is contained in a single circular molecule called the bacterial chromosome. When DNA polymerase is described as extending what does that mean The DNA strand from BIOLOGY 1101 at East Carteret High. The name describes what the molecule is.
Either A T C or G. DNA is necessary for the production of proteins. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and is one of the two types of nucleic acid found in our cells.
Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA is a molecule that contains the biological instructions that make each species unique. Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. DNA deoxyribonucleic acid is one of the two types of genetic material that exists in every organism including single-celled organisms viruses and bacteria the other being RNA.
Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA is a molecule that contains the biological instructions that make each species unique. The general procedure includes. DNA is beautifully intricate and.
Every organism s DNA consists of a unique. All living things have DNA within. DNA is one of two major classes of molecules the other is RNA.
DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter. DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms.

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks

Pin By Steve Mathews On Science Biology Worksheet Prokaryotes Cells Worksheet
No comments for "How Is Dna Described and What Does This Mean"
Post a Comment